Our bodies change a lot as we get older, and it can be harder to control body fat for women over 50.
Not all body fat is created equal.
It is possible for the body to store different kinds of fat, and each has its own properties, risks, and ways to get rid of it. Being aware of the different kinds of body fat is important for creating a weight loss plan and improving health in general.
When it comes to body fat, scientists typically categorize it into six main types: visceral fat, subcutaneous fat, essential fat, brown fat, beige fat, and ectopic fat. Each type plays a unique role in how our body functions, stores energy, and even maintains warmth.
While these scientific terms give us an understanding of fat distribution, they don’t always resonate with the real-life experience of women over 50.
That’s why we’ll focus on the types of body fat that are more relatable to our day-to-day lives and how they appear on our bodies. From full body fat to swollen bellies, and the ever-challenging lower body fat, we’re breaking it down in a way that speaks to what we truly experience.
Let’s take a closer look at the six types of body fat, their causes, and how to eliminate them.
1. Full Upper Body Fat
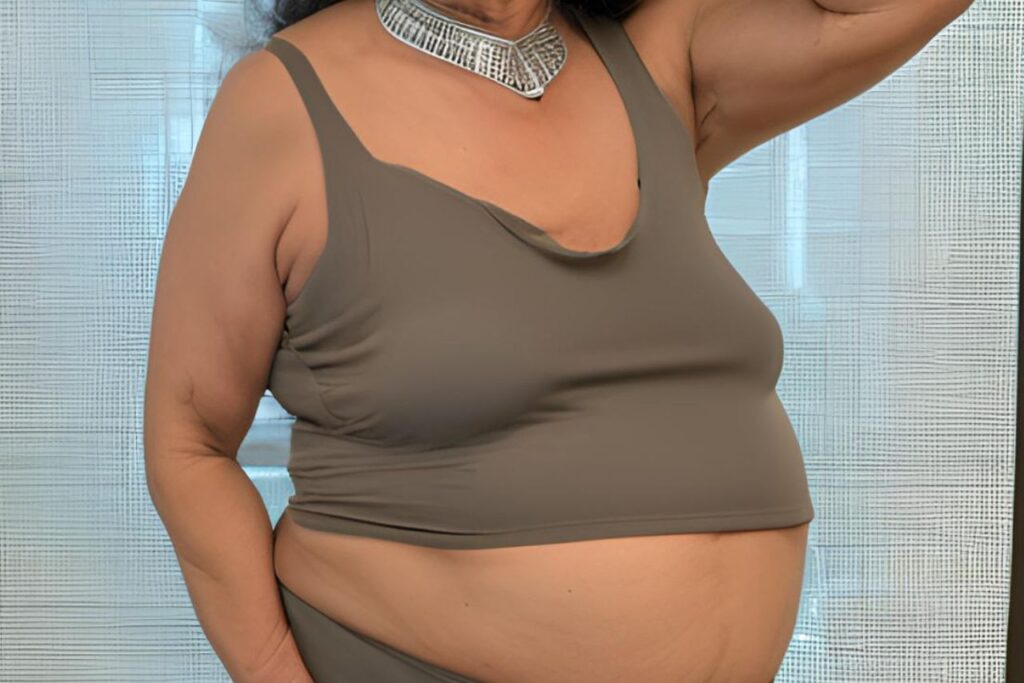

Overeating, especially excessive consumption of sugary foods and processed carbohydrates, is typically the cause of full upper body fat.
This type of fat tends to accumulate around the arms, chest, and upper back.
It is also linked to a sedentary lifestyle, making it common in individuals who consume more calories than they burn.
Menopause brings about significant hormonal shifts, including a decrease in estrogen. This can also lead to a redistribution of fat towards the midsection and upper body.
“Full body fat generally refers to an overall increase in fat throughout the body, often linked to subcutaneous fat, which is stored just beneath the skin. Subcutaneous fat is the layer that creates a soft appearance on the arms, legs, and torso. While it is essential for insulating the body, excess amounts can accumulate over time, contributing to a heavier overall appearance.“
How to Lose Full Upper Body Fat
While there’s no guaranteed way to spot-reduce fat, a combination of healthy lifestyle changes can help reduce overall body fat, including in the upper body.
The key to losing upper body fat is creating a calorie deficit.
Consuming fewer processed and sugary foods and focusing on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help you achieve this.
Regular cardiovascular exercise, such as running, swimming, or brisk walking, helps burn excess calories, while strength training builds lean muscle, which in turn increases metabolism and aids fat loss.
READ ALSO: Why Women Gain Belly Fat Over Age 50

2. Swollen Belly
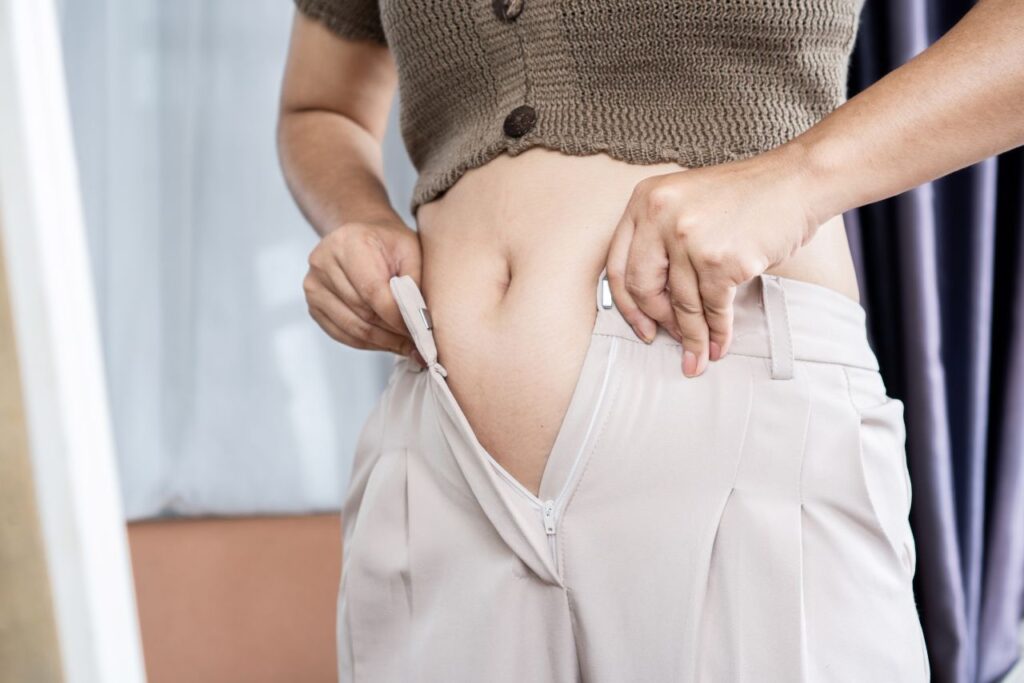

Menopause-related hormonal changes, digestive problems, and lifestyle choices are just a few of the factors that can contribute to a swollen belly in women over 50.
As estrogen levels decline, the body tends to store more fat around the abdomen. Additionally, menopause can slow down the digestive system, leading to bloating and water retention.
Poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity can also contribute to a swollen belly.
In some cases, underlying health conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or food intolerances can exacerbate the problem.
This type of fat can also lead to other health problems, including liver damage and digestive issues.
“A swollen or bloated belly is often connected to visceral fat, which is stored deep within the abdominal cavity around organs like the liver and intestines. Visceral fat is considered the most dangerous type because it’s associated with an increased risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other health issues. For many women over 50, this type of fat tends to accumulate in the belly as hormone levels change.“
How to Lose Swollen Belly Fat
The most effective way to reduce a swollen stomach is to cut back on or eliminate alcohol consumption.
Replacing alcohol with hydrating beverages like water and herbal teas can help flush out toxins and reduce bloating.
Treating any underlying health conditions, like sleep apnea or asthma, is necessary if breathing problems are making the issue worse.
Additionally, a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as leafy greens, berries, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce abdominal swelling.
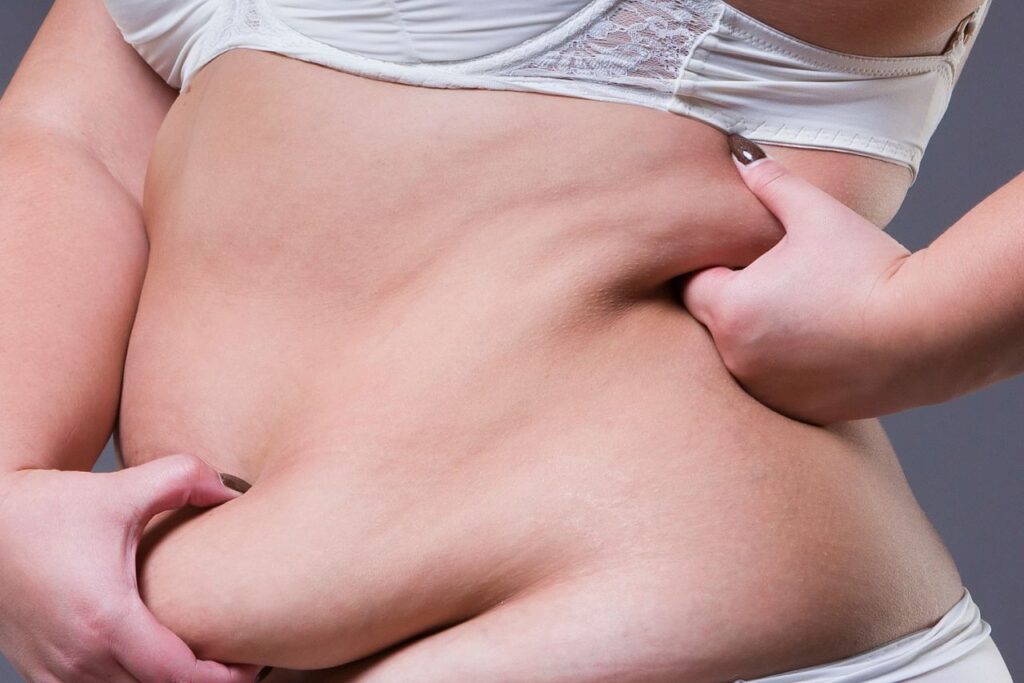
3. Lower Belly Fat
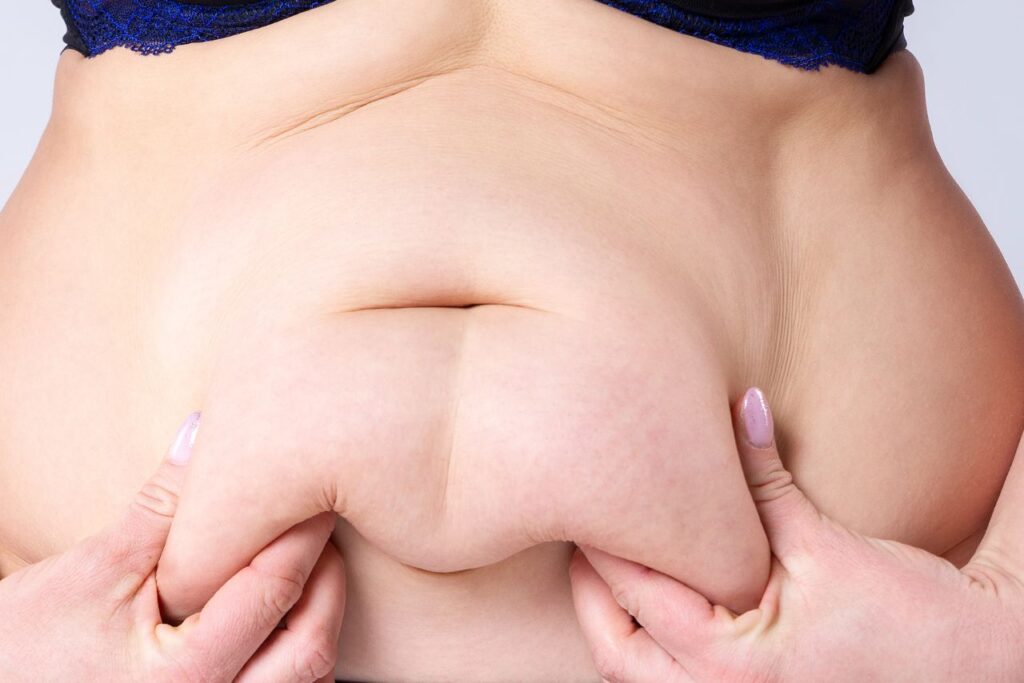
Lower belly fat is often caused by stress, depression, and anxiety. It’s often referred to as “pooch” or “muffin top,” which can be a frustrating concern for many women over 50.
When you are under a lot of stress for a long time, your body releases cortisol, a hormone that makes you store fat, especially around your stomach.
This type of fat is more than just a cosmetic concern. It can lead to serious health issues such as insulin resistance and increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
“Lower belly fat often builds up due to an excess of both visceral fat and subcutaneous fat in the abdominal region. While visceral fat causes swelling deeper in the belly, subcutaneous fat forms just under the skin, leading to that stubborn pouch below the belly button that can be hard to shed.”
How to Lose Lower Belly Fat
Reducing stress is essential to losing lower abdomen fat. For example, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and meditation are all good ways to deal with stress.
In addition, eating a diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats helps stabilize blood sugar levels, which can reduce the production of cortisol.
Regular physical activity, especially high-intensity interval training (HIIT), is effective at burning belly fat and improving mental health.
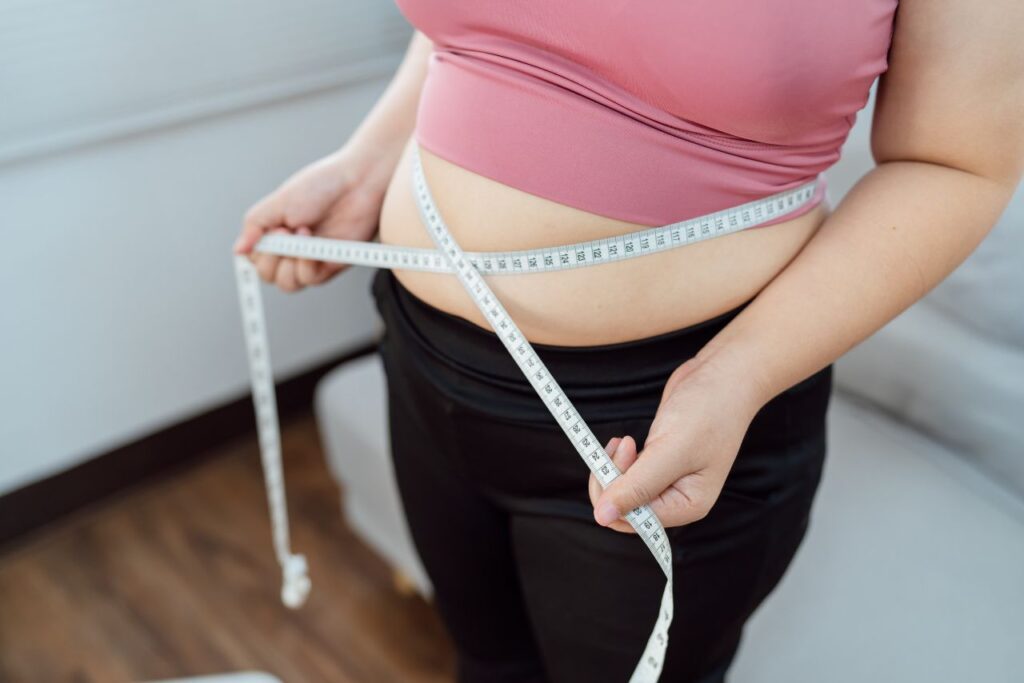
4. Big Belly with Upper Back Fat

Inactivity is typically the cause of a big belly and upper back fat. Women who lead a sedentary lifestyle are more prone to accumulating fat in these areas.
This type of fat is particularly stubborn and may also be associated with poor posture, which can cause the back to store more fat as muscles weaken.
“A large belly that also affects the lower back can be a combination of subcutaneous fat and visceral fat, especially when weight gain extends to the back. Ectopic fat can also contribute here—this is fat stored in abnormal places, such as within muscles or organs, which can lead to a thicker appearance in the midsection and back area.“
How to Lose Big Belly and Upper Back Fat
Getting more active is important if you want to lose fat in your belly and upper back.
Cardio exercises, like swimming, cycling, or walking, can help burn fat all over the body. Strength training exercises, like push-ups, rows, and planks, work the muscles in the upper back and core.
It’s also important to maintain an active lifestyle by avoiding long periods of sitting. A diet rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats will support overall fat loss while reducing the intake of refined sugars and processed foods.

5. Lower Body Fat

An excess of gluten in the diet frequently contributes to lower body fat, particularly around the hips and thighs. It’s often referred to as “saddlebags” or “banana bread,” which can be a common concern.
Studies have shown that the decline in estrogen during menopause can contribute to the redistribution of fat to the hips and thighs.
Estrogen plays a crucial role in regulating fat storage, and when its levels drop during menopause, the body tends to store fat in the lower body.
This shift can result in an increased accumulation of fat around the hips, thighs, and sometimes the abdomen, making it more challenging for women to maintain their pre-menopausal body shape.
Foods such as bread, pasta, and other whole grains can also contribute to fat accumulation in this area, especially in people sensitive to gluten.
“Lower body fat—especially on the hips, thighs, and buttocks—can be linked to subcutaneous fat as well as essential fat, which is necessary for normal body function. Women naturally store more fat in these areas due to estrogen, but excess amounts can become problematic over time, especially after menopause.“
How to Lose Lower Body Fat
Consider cutting back on gluten-containing foods and, if necessary, switching to a gluten-free diet to lose lower body fat.
This includes eating more gluten-free grains like quinoa, rice, and corn, as well as increasing the intake of vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Leg-targeting exercises like squats, lunges, and cycling can help tone the lower body and accelerate fat loss.
READ ALSO: 10 Fat-Burning Foods To Keep Women Over 50 Healthy
6. Lower Legs Fat
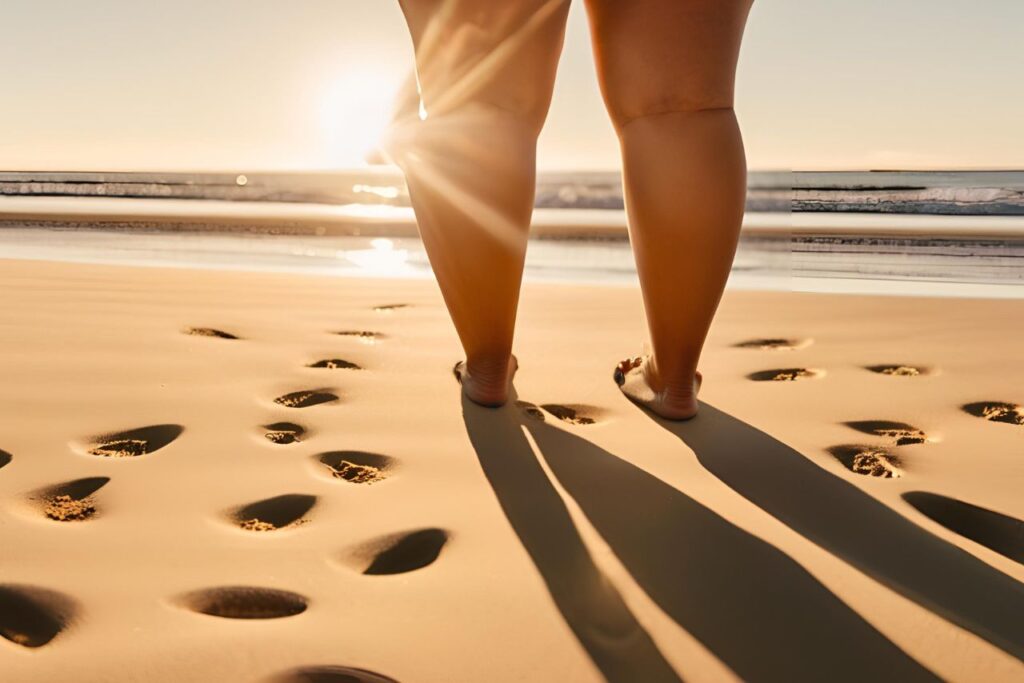

Lower legs fat in women over 50 is often caused by poor circulation, fluid retention, and hormonal changes due to menopause.
As estrogen levels decline, the body can store more fat in areas like the legs. A sedentary lifestyle and doing less physical activity can also cause fat to build up in the lower legs.
This problem can also be caused by genes and muscle loss that comes with getting older, as the body’s metabolism slows down and fat builds up more easily.
Diet and eating too much sodium, which can make you retain water, may make fat in the lower legs look even worse.
“Fat that builds up in the lower legs, often around the calves and ankles, is typically subcutaneous fat. However, as we age, there’s a possibility of ectopic fat accumulating around the lower body muscles, which can make legs appear heavier or swollen. In some cases, issues like poor circulation or fluid retention might also contribute.“
How to Lose Lower Legs Fat
While hereditary fat can be difficult to lose, regular exercise that targets the lower body can help tone and reduce fat in this area.
Strength training exercises such as lunges, leg presses, and step-ups can help strengthen the muscles in the lower body and reduce fat over time.
Eat a balanced diet rich in whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Reducing refined carbs, sugary foods, and sodium can help minimize fat storage and reduce water retention in the lower legs.
Drink enough water to flush out excess fluids and toxins to reduce bloating and fluid retention in the legs.
Closing Thoughts
The first step to a healthier body, especially for people over 50, is to learn about the different kinds of body fat and what causes them.
You can lose fat, improve your health, and make your overall well-being better by focusing on the causes of each type of fat and making targeted changes to your lifestyle.
Furthermore, you should limit your alcohol intake and stop smoking cigarettes.
Whether it is by making changes to your diet, working out regularly, or dealing with stress, the important thing is to be consistent and take action.
♡ Love ♡,
Ready to say goodbye to that stubborn body fat? Join our exclusive 14-Day Lose Belly Fat Challenge designed for women over 50 to help you slim down, boost your energy, and feel your best.
With simple exercises, a balanced meal plan, and stress-relieving practices, you’ll see results in no time!
Don’t miss out! Join challenge now and start your journey to a toned and lean body.



















